2018 Volume No 36 – pages 128-141
Title: Autologous bilayered self-assembled skin substitutes (SASSs) as permanent grafts: a case series of 14 severely burned patients indicating clinical effectiveness |
Authors: L Germain, D Larouche, B Nedelec, I Perreault, L Duranceau, P Bortoluzzi, C Beaudoin Cloutier, H Genest, L Caouette-Laberge, A Dumas, A Bussière, E Boghossian, J Kanevsky, Y Leclerc, J Lee, MT Nguyen, V Bernier, BM Knoppers8, VJ Moulin, FA Auger |
Address: CHU de Québec-Université Laval, LOEX, Aile-R, 1401 18ième Rue, Quebec, Quebec, G1J 1Z4, Canada |
E-mail: lucie.germain at fmed.ulaval.ca |
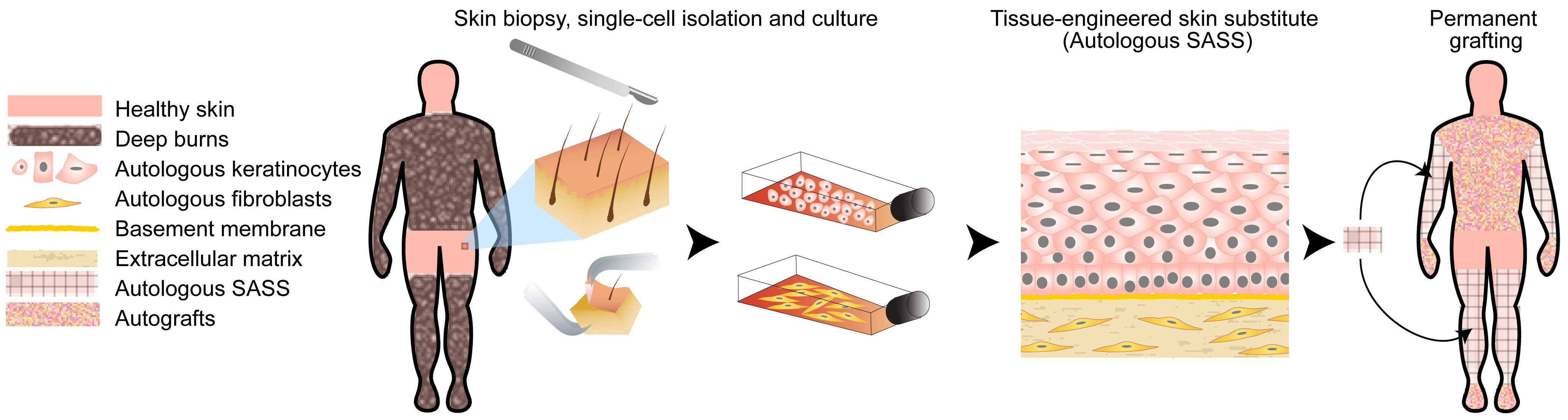
Abstract: Split-thickness skin autografts (AGs) are the standard surgical treatment for severe burn injuries. However, the treatment of patients with substantial skin loss is limited by the availability of donor sites for skin harvesting. As an alternative to skin autografts, our research group developed autologous self-assembled skin substitutes (SASSs), allowing the replacement of both dermis and epidermis in a single surgical procedure. The aim of the study was to assess the clinical outcome of the SASSs as a permanent coverage for full-thickness burn wounds. Patients were recruited through the Health Canada’s Special Access Program. SASSs were grafted on debrided full-thickness wounds according to similar protocols used for AGs. The graft-take and the persistence of the SASS epithelium over time were evaluated. 14 patients received surgical care with SASSs. The mean percentage of the SASS graft-take was 98 % (standard deviation = 5) at 5 to 7 d after surgery. SASS integrity persisted over time (average follow-up time: 3.2 years), without noticeable deficiency in epidermal regeneration. Assessment of scar quality (skin elasticity, erythema, thickness) was performed on a subset of patients. Non-homogeneous pigmentation was noticed in several patients. These results indicated that the SASS allowed the successful coverage of full-thickness burns given its high graft-take, aesthetic outcome equivalent to autografting and the promotion of long-term tissue regeneration. When skin donor sites are in short supply, SASSs could be a valuable alternative to treat patients with full-thickness burns covering more than 50 % of their total body surface area. |
Key Words: Autologous, burn, culture techniques, connective tissue, regenerative medicine, skin, skin grafts, tissue culture, tissue engineering, tissue therapy. |
Publication date: September 13th 2018 |
Article download: Pages
128-141 (PDF file) |