2021 Volume No 41 – pages 204-215
Title: Effect of extracellular matrix and dental pulp stem cells on bone regeneration with 3D printed PLA/HA composite scaffolds |
Authors: I Gendviliene, E Simoliunas, M Alksne, S Dibart, E Jasiuniene, V Cicenas, R Jacobs, V Bukelskiene, V Rutkunas |
Address: Vilnius University, Zalgirio g. 117, LT- 08217, Vilnius,
Lithuania |
E-mail: ieva.gendviliene at gmail.com |
Abstract: The demand for bone grafting procedures in various fields of medicine is increasing. Existing substitutes in
clinical practice do not meet all the criteria required for an ideal bone scaffold, so new materials are being
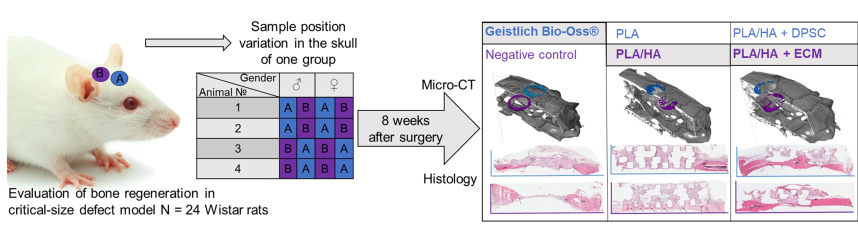
sought. This study evaluated bone regeneration using a critical-size Wistar rat’s calvarial defect model. 12
male and 12 female rats were evenly divided into 3 groups: 1. Negative and positive (Geistlich Bio-Oss®) controls; 2. polylactic acid (PLA) and PLA/hydroxyapatite (HA); 3. PLA/HA cellularised with dental pulp
stem cells (DPSC) and PLA/HA extracellular matrix (ECM) scaffolds. PLA/HA filament was created using
hot-melt extrusion equipment. All scaffolds were fabricated using a 3D printer. DPSC were isolated from the
incisors of adult Wistar rats. The defects were evaluated by micro-computed tomography (µCT) and histology,
8 weeks after surgery. µCT revealed that the Bio-Oss group generated 1.49 mm3 and PLA/HA ECM 1.495 mm3
more bone volume than the negative control. Histology showed a statistically significant difference between
negative control and both (Bio-Oss and PLA/HA ECM) groups in rats of both genders. Moreover, histology
showed gender-specific differences in all experimental groups and a statistically significant difference between
cellularised PLA/HA and PLA/HA ECM groups in female rats. Qualitative histology showed the pronounced
inflammation reaction during biodegradation in the PLA group. In conclusion, the bone-forming ability was
comparable between the Bio-Oss and PLA/HA ECM scaffolds. Further research is needed to analyse the
effects of ECM and PLA/HA ratio on osteoregeneration. |
Key Words: Biocomposite scaffolds, extracellular matrix, PLA/HA scaffolds, bone regeneration, dental pulp
stem cells, Geistlich Bio-Oss, micro-computer tomography, histology.
|
Publication date: February 28th 2021 |
Article download: Pages
204-215 (PDF file) |