2025 Volume No 53 – pages 52-64
Title: Progress in the application of microneedle-mediated cell implantation combined with artificial dermal scaffolds |
Authors: ZF Wu, W Cheng, JD Su |
Address: Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, Suzhou Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, 215000 Suzhou, Jiangsu, China |
E-mail: jiandongsu at njmu.edu.cn |
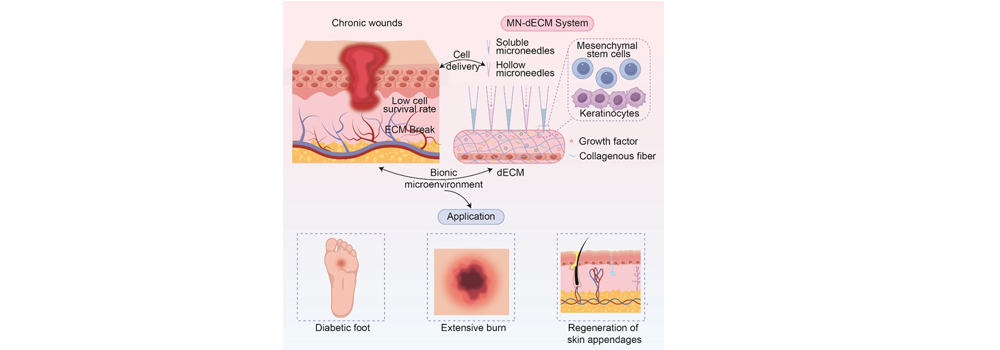
Abstract: Tissue-engineered skin represents a transformative approach for treating chronic wounds and extensive burns; however, challenges such as low cell survival rates and insufficient microenvironmental support remain. This review highlights the synergistic potential of microneedle (MN)-mediated cell implantation and decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) scaffolds in addressing these limitations. MNs enable minimally invasive, targeted delivery of therapeutic cells (e.g., mesenchymal stem cells, keratinocytes) into the skin layers, while dECM scaffolds provide a biomimetic microenvironment rich in collagen and growth factors that enhance cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. We critically analyze (1) MN designs (e.g., hollow, soluble) optimized for skin-compatible cell delivery; (2) advanced dECM fabrication techniques that preserve extracellular matrix (ECM) bioactivity; and (3) emerging combinatorial strategies in which MN-delivered cells integrate with dECM to accelerate wound closure and functional skin regeneration. By bridging precise delivery with microenvironmental engineering, this integrated platform offers a scalable solution for clinical translation, with applications extending to chronic wound repair, appendage-bearing skin models, and immunotherapy. |
Keywords: Microneedles, cell implantation, decellularization, tissue-engineered skin, regeneration medicine. |
Publication date: 31st October 2025 |
Copyright policy: © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Forum Multimedia Publishing, LLC. This article is distributed in accordance with Creative Commons Attribution Licence (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). |
Article download: Pages 52-64 (PDF file) |